
Is Keto Diet Healthy?

Is Keto Diet Healthy?
A Keto diet is an eating plan that focuses on foods that provide a lot of healthful fats, adequate amounts of protein, and very few carbohydrates. The goal is to get more calories from fat than from carbs. The diet works by depleting the body of its sugar reserves. As a result, it will start to break down fat for energy. These results in the production of molecules called ketones that the body uses for fuel. When the body burns fats, it can also lead to weight loss. There are several types of Keto diet, including the Standard Ketogenic Diet and the Cyclical Ketogenic Diet. In this article from https://bestketodietforme.com/, we explain the benefits of the Keto diet, as well as its risks.
1. Supports weight loss
The ketogenic diet may help promote weight loss in several ways, including boosting metabolism and reducing appetite. Ketogenic diets consist of foods that fill a person up and may reduce hunger-stimulating hormones. For these reasons, following a Keto diet may reduce appetite and promote weight loss. In a 2013 meta-analysis of 13 different randomized controlled trials, researchers found that people following ketogenic diets lost 2 pounds (lbs) more than those following low fat diets over 1 year.
Similarly, another review of 11 studies demonstrated that people following a ketogenic diet lost 5 lbs more than those following low-fat diets after 6 months. Here, learn about the difference between a Keto and Atkins diet plan.

2. Improves acne

Acne has several different causes and may have links to diet and blood sugar in some people. Eating a diet high in processed and refined carbohydrates may alter the balance of gut bacteria and cause blood sugar to rise and fall significantly, both of which can adversely affect skin health. According to a 2012 study, by decreasing carb intake, a ketogenic diet could reduce acne symptoms in some people.
3. May reduce risk of certain cancers

Researchers have examined the effects of the ketogenic diet in helping prevent or even treat certain cancers. One study found that the ketogenic diet may be a safe and suitable complementary treatment to use alongside chemotherapy and radiation therapy in people with certain cancers. This is because it would cause more oxidative stress in cancer cells than in normal cells, causing them to die. A more recent study from 2018 suggests that because the ketogenic diet reduces blood sugar, it could also lower the risk of insulin complications. Insulin is a hormone that controls blood sugar that may have links to some cancers.
Although some research indicates that the ketogenic diet may have some benefit in cancer treatment, studies in this area are limited. Researchers need to carry out more studies to fully understand the potential benefits of the ketogenic diet in cancer prevention and treatment.
4. May improve heart health
When a person follows the ketogenic diet, it is important that they choose healthful foods. Some evidence shows that eating healthful fats, such as avocados instead of less healthful fats, such as pork rinds, can help improve heart health by reducing cholesterol. A 2017 review of studies of animals and humans on a Keto diet showed that some people experienced a significant drop in levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL), or bad cholesterol, and triglycerides, and an increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL), or “good” cholesterol.
High levels of cholesterol can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. A keto diet’s reducing effect on cholesterol may, therefore, reduce a person’s risk of heart complications. However, the review concluded that the positive effects of the diet on heart health depend on diet quality. Therefore, it’s important to eat healthful, nutritionally balanced food while following the keto diet.
5. May protect brain function

Some studies, such as this 2019 review, suggest the ketones that generate during the Keto diet provide neuroprotective benefits, which means they can strengthen and protect the brain and nerve cells.
For this reason, a Keto diet may help a person prevent or manage conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease. However, more research is necessary into a Keto diet’s effects on the brain.
6. Potentially reduces seizures
The ratio of fat, protein, and carbs in a Keto diet alters the way the body uses energy, resulting in ketosis. Ketosis is a metabolic process during which the body uses ketone bodies for fuel.
The Epilepsy Foundation suggest that ketosis can reduce seizures in people with epilepsy — especially those who have not responded to other treatment methods. More research is necessary on how effective this is, though it seems to have the most effect on children who have focal seizures.
A 2019 review supports the hypothesis that a Keto diet can support people with epilepsy. The ketogenic diet may reduce epilepsy symptoms by several different mechanisms.
7. Improves PCOS symptoms
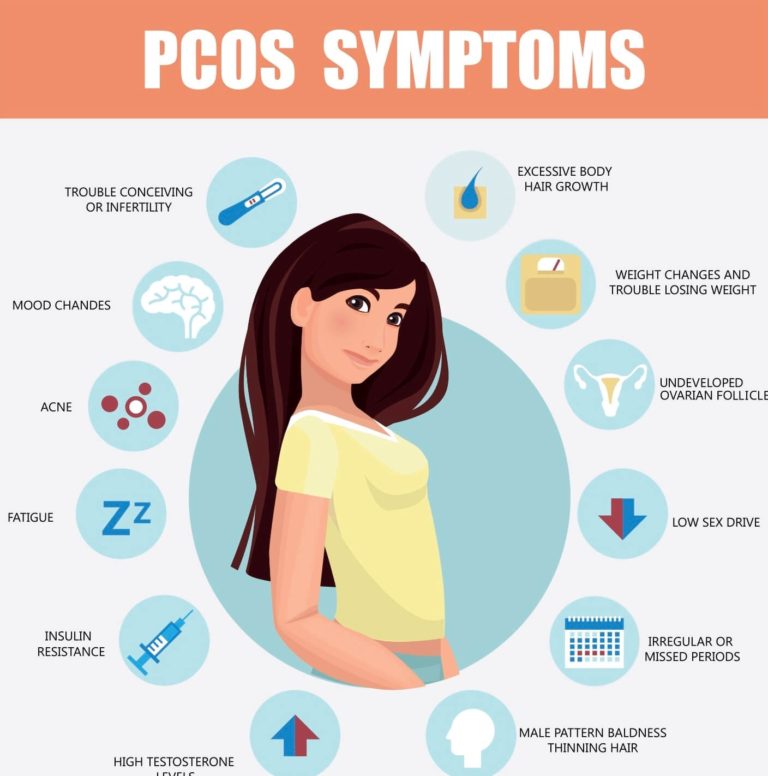
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that can lead to excess male hormones, ovulatory dysfunction, and polycystic ovaries.
A high-carbohydrate diet can cause adverse effects in people with PCOS, such as skin problems and weight gain. There are not many clinical studies on the ketogenic diet and PCOS. One pilot study from 2005 examined five women over 24 weeks.
The researchers found that a ketogenic diet improved several markers of PCOS, including: weight loss, hormone balance, ratios of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), levels of fasting insulin
A different review of studies from 2019 found that a Keto diet had beneficial effects for people with hormonal disorders, including PCOS and type 2 diabetes. However, they did also caution that the studies were too diverse to recommend a Keto diet as a general treatment for PCOS.
Risks and complications
The ketogenic diet may have a range of health benefits. However, staying on the ketogenic diet long-term can have an adverse effect on health, including an increased risk of the following health problems: kidney stones, excess protein in the blood, mineral and vitamin deficiencies, a buildup of fat in the liver.
The Keto diet can cause adverse side effects that many people know as Keto flu. These adverse effects may include: constipation, fatigue, low blood sugar, nausea, vomiting, headaches, a low tolerance for exercise. These symptoms are especially common at the beginning of the diet as the body adjusts to its new energy source. Some populations should avoid the Keto diet, including: people with diabetes who are insulin-dependent, people who have eating disorders, those with kidney disease or pancreatitis, women during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
People who take a type of medication called sodium-glucose co transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for type 2 diabetes should also not follow a Keto diet. This medication increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, a dangerous condition that increases acidity in the blood.
